Image Annotation Tool for Teams
Annotate is an advanced image annotation tool supporting complex taxonomies and teamwork on computer vision projects.
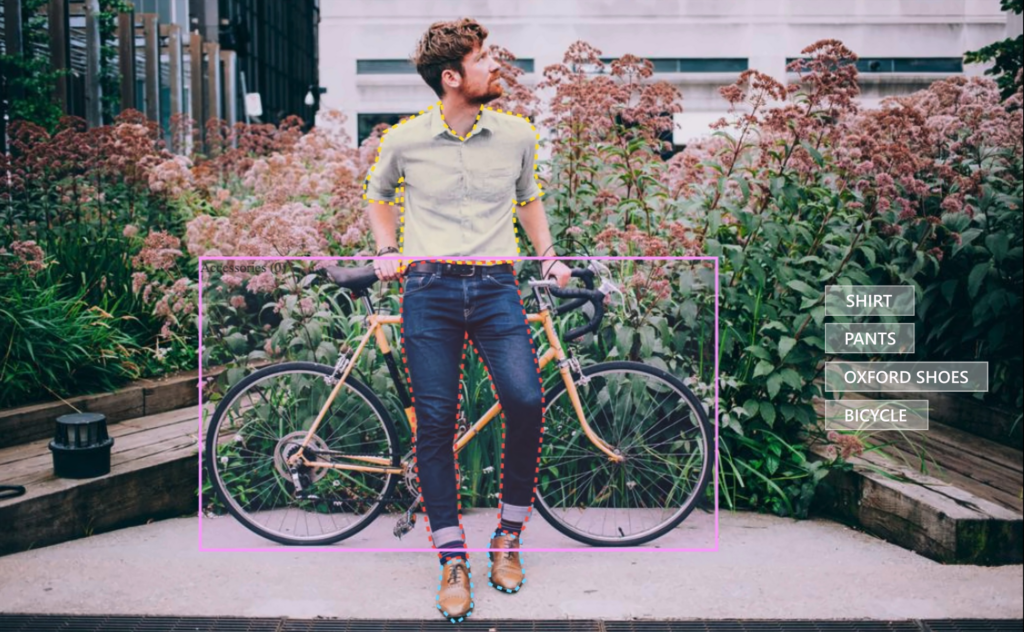


Through the years, we worked with many annotation tools. The problem is most of the desktop annotating apps are offline and intended for single-person use, not for team cooperation. The web-based apps, on the other hand, mostly focus on data management with photo annotation, and not on the whole ecosystem with API and inference systems. In this article, I review, what should a good image annotation tool do, and explain the basic features of our own tool – Annotate.
Every big machine learning project requires the active cooperation of multiple team members – engineers, researchers, annotators, product managers, or owners. For example, supervised deep learning for object detection, as well as segmentation, outperforms unsupervised solutions. However, it requires a lot of data with correct annotations. Annotation of images is one of the most time-consuming parts of every deep learning project. Therefore, picking the right annotator tool is critical. When your team is growing and your projects require higher complexity over time, you may encounter new challenges, such as:
- Adding labels to the taxonomy would require re-checking a lot of your work
- Increasing the performance of your models would require more data
- You will need to monitor the progress of your projects
Building solid annotation software for computer vision is not an easy task. And yes, it requires a lot of failures and taking many wrong turns before finding the best solution. So let’s look at what should be the basic features of an advanced data annotation tool.
What Should an Advanced Image Annotation Tool Do?
Many customers are using our cloud platform Ximilar App in very specific areas, such as Fashion, Healthcare, Security, or Industry 4.0. The environment of a proper AI helper or tool should be complex enough to cover requirements like:
- Features for team collaboration – you need to assign tasks, and then check the quality and consistency of data
- Great user experience for dataset curation – everything should be as simple as possible, but no simpler
- Fast production of high-quality datasets for your machine-learning models
- Work with complex taxonomies & many models chained with Flows
- Fast development and prototyping of new features
- Connection to Rest API with Python SDK & querying annotated data
With these needs in mind, we created our own image annotation tool. We use it in our internal projects and provide it to our customers as well. Our technologies for machine learning accelerate the entire pipeline of building good datasets. Whether you are a freelancer tagging pictures or a team managing product collections in e-commerce, Annotate can help.
Our Visual AI tools enable you to work with your own custom taxonomy of objects, such as fashion apparel or things captured by the camera. You can read the basics on the categories & tags and machine learning model training, watch the tutorials, or check our demo and see for yourself how it works.
The Annotate
Annotate is an advanced image annotation tool, which enables you to annotate images precisely and fast. It works as an end-to-end platform for visual data management. You can query the same images, change labels, create objects, draw bounding boxes and even polygons here.
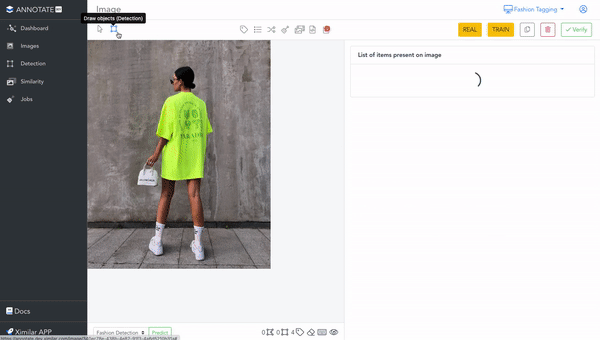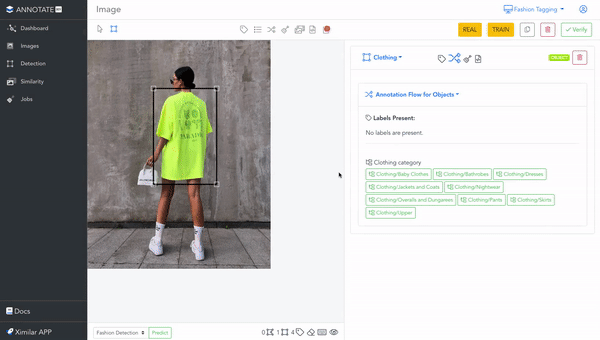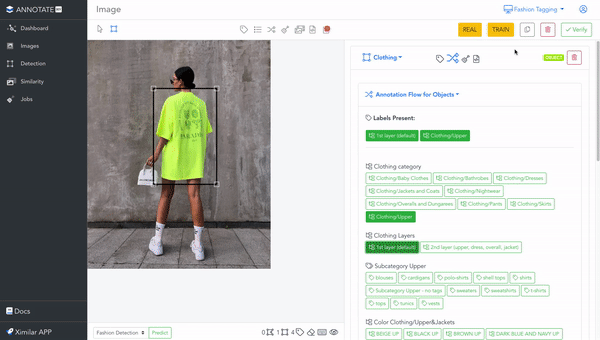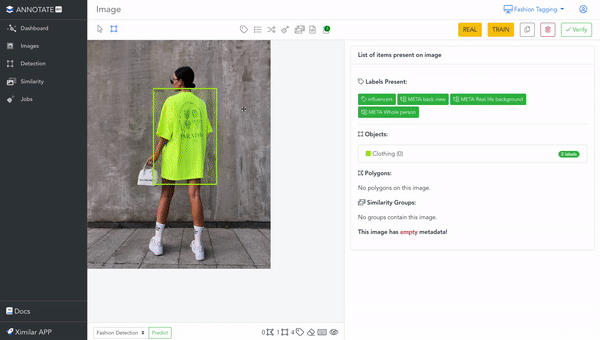
It is a web-based online annotation tool, that works fully on the cloud. Since it is connected to the same back-end & database as Ximilar App, all changes you do in Annotate, manifest in your workspace in App, and vice versa. You can create labels, tasks & models, or upload images through the App, and use them in Annotate.
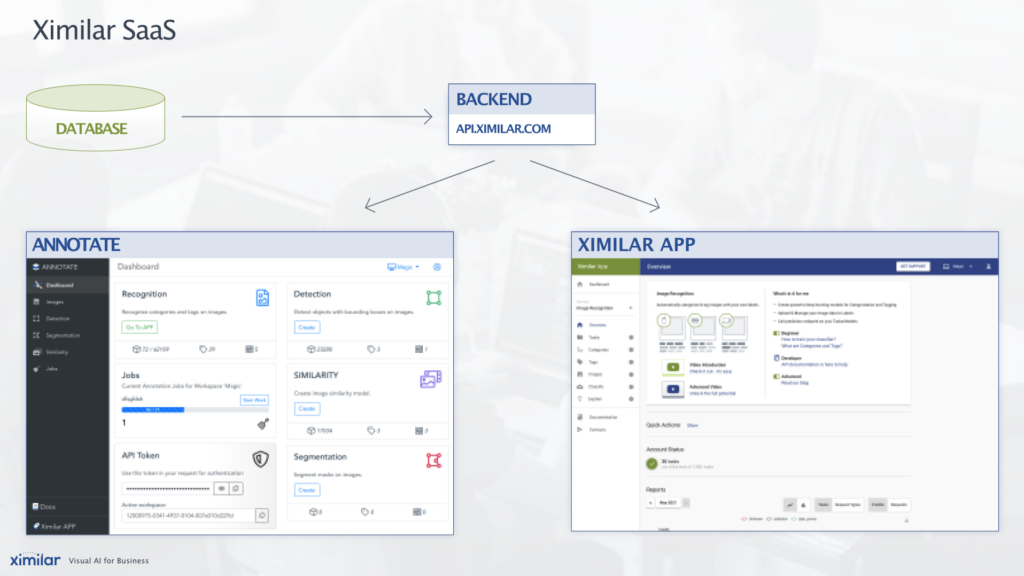
Annotate extends the functionalities of the Ximilar App. The App is great for training, creating entities, uploading data, and batch management of images (bulk actions for labelling and filtering). Annotate, on the other hand, was created for the detail-oriented management of images. The default single-zoomed image view brings advantages, such as:
- Identifying separate objects, drawing polygons and adding metadata to a single image
- Suggestions based on AI image recognition help you choose from very complex taxonomies
- The annotators focus on one image at a time to minimize the risk of mistakes
Interested in getting to know Annotate better? Let’s have a look at its basic functions.
Deep Focus on a Single Image
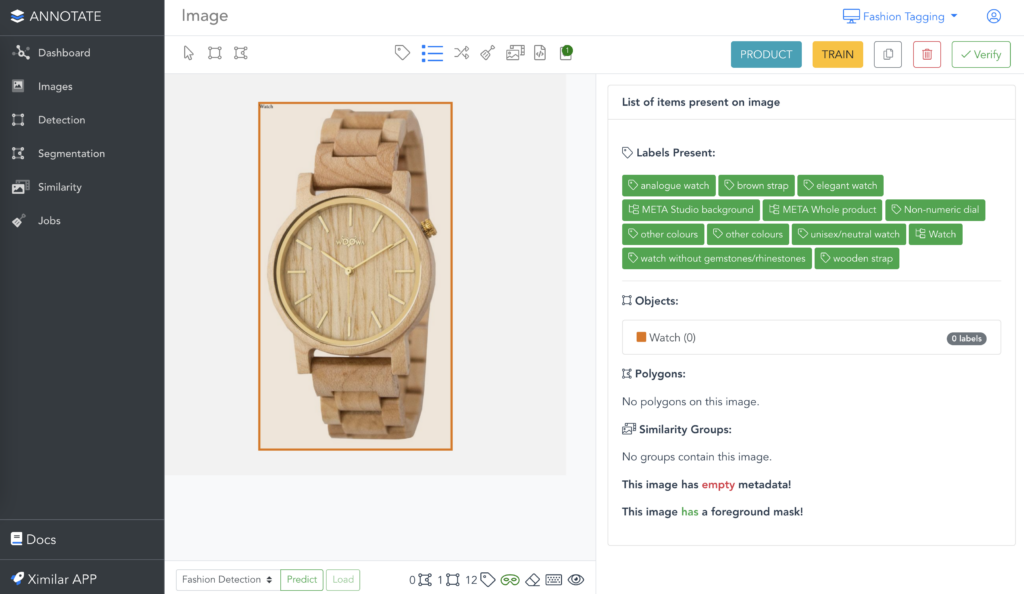
If you enter the Images (left menu), you can open any image in the single image view. To the right of the image, you can see all the items located in it. This is where most of the labelling is done. There is also a toolbar for drawing objects and polygons, labelling images, and inspecting metadata.
In addition, you can zoom in/out and drag the image. This is especially helpful when working with smaller objects or big-resolution images. For example, teams annotating medical microscope samples or satellite pictures can benefit from this robust tool.
Create Multiple Workspaces
Some of you already know this from other SaaS platforms. The idea is to divide your data into several independent storages. Imagine your company is working on multiple projects at the same time and each of them requires you to label your data with an image annotation tool. Your company account can have many workspaces, each for one project.

Within the workspaces, you don’t mix your images, labels, and tasks. For example, one workspace contains only images for fruit recognition projects (apples, oranges, and bananas) and another contains data on animals (cats and dogs).
Your team members can get access to different workspaces. Also, everyone can switch between the workspaces in the App as well as in Annotate (top right, next to the user icon). Did you know, that the workspaces are also accessible via API? Check out our documentation and learn how to connect to API.
Train Precise AI Models with Verification
Building good computer vision models requires a lot of data, high-quality annotations, and a team of people who understand the process of building such a dataset. In short, to create high-quality models, you need to understand your data and have a perfectly annotated dataset. In the words of the Director of AI at Tesla, Andrej Karpathy:
Annotate helps you build high-quality AI training datasets by verification. Every image can be verified by different users in the workspace. You can increase the precision by training your models only on verified images.
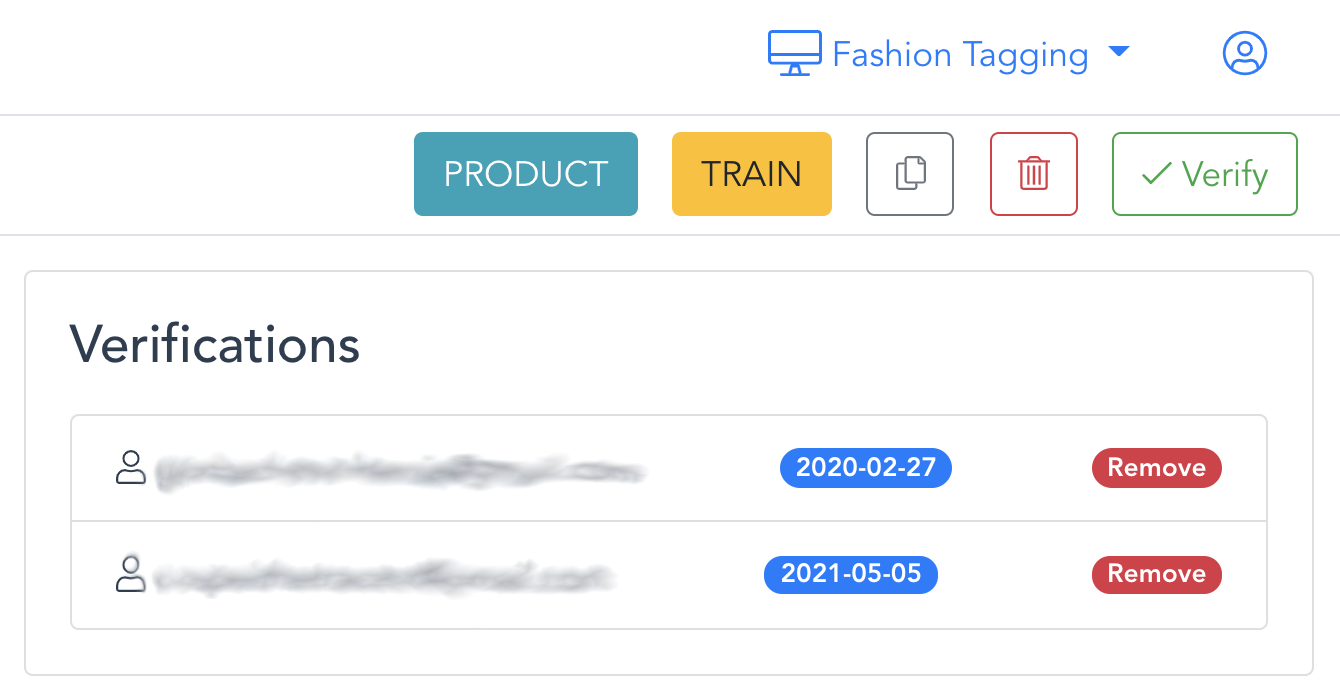
Verifying your data is a necessary requirement for the creation of good deep-learning models. To verify the image, simply click the button verify or verify and next (if you are working on a job). You will be able to see who verified any particular image and when.
Create and Track Image Annotating Jobs
When you need to process the newly uploaded images, you can assign them to a Job and a team of people can process them one by one in a job queue. You can also set up exactly how many times each image should be seen by the people processing this queue.
Moreover, you can specify, which photo recognition model or flow of models should be displayed when doing the job. For example, here is the view of the jobs that we are using in one of our tagging services.
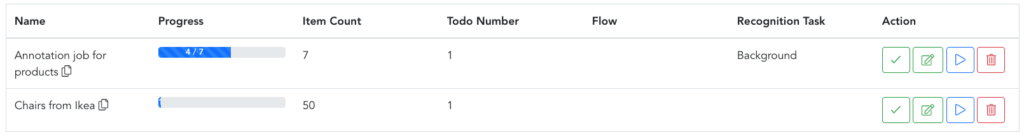
you can start working by hitting the play button on the right
When working on a job, every time an annotator hits the Verify & Next button, it will redirect them to a new image within a job. You can track the progress of each job in the Jobs. Once the image annotation job is complete, the progress bar turns green, and you can proceed to the next steps: retraining the models, uploading new images, or creating another job.
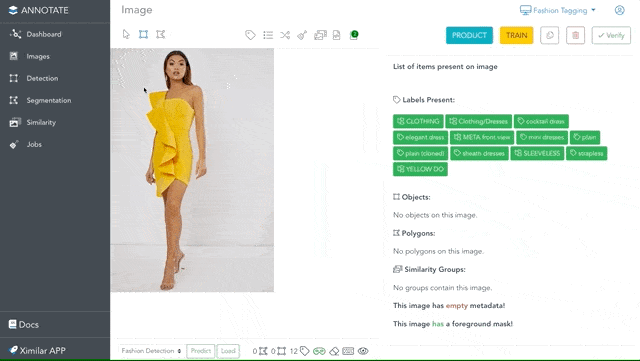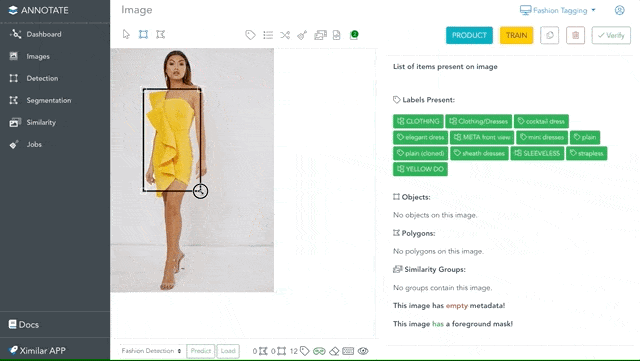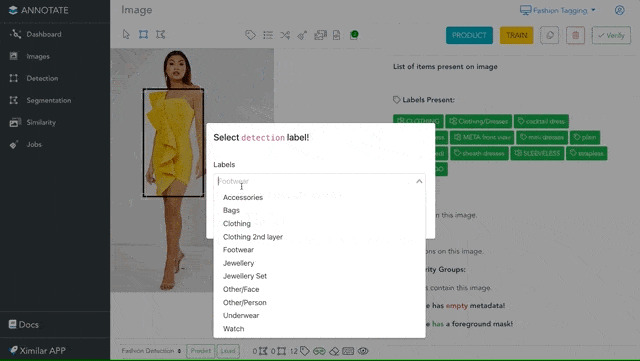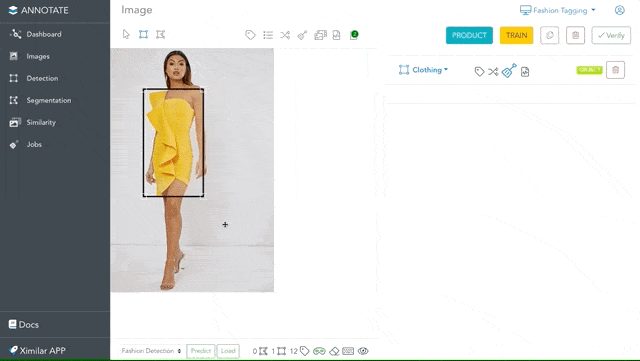
Draw Objects and Polygons
Sometimes, recognizing the most probable category or tags for an image is not enough. That is why Annotate provides a possibility to identify the location of specific things by drawing objects and polygons. The great thing is that you are not paying any credits for drawing objects or labelling. This makes Annotate one of the most cost-effective online apps for image annotation.
What exactly do you pay for, when annotating data? The only API credits are counted for data uploads, with volume-based discounts. This makes Annotate an affordable, yet powerful tool for data annotation. If you want to know more, read our newest Article on API Credit Packs, check our Pricing Plans or Documentation.
Annotate With Complex Taxonomies Elegantly
The greatest advantage of Annotate is working with very complex taxonomies and attribute hierarchies. That is why it is usually used by companies in E-commerce, Fashion, Real Estate, Healthcare, and other areas with rich databases. For example, our Fashion tagging service contains more than 600 labels that belong to more than 100 custom image recognition models. The taxonomy tree for some of the biotech projects can be even broader.
Navigating through the taxonomy of labels is very elegant in Annotate – via Flows. Once your Flow is defined (our team can help you with it), you simply add labels to the images. The branches expand automatically when you add labels. In other words, you always see only essential labels for your images.
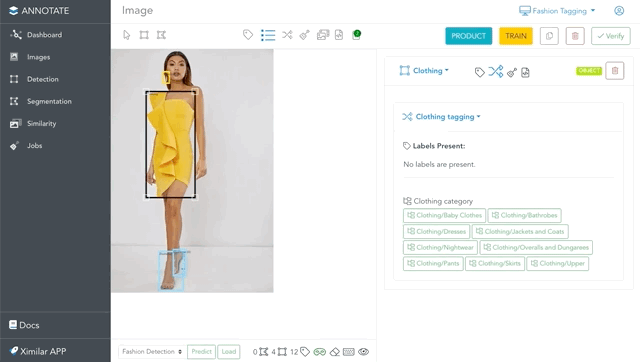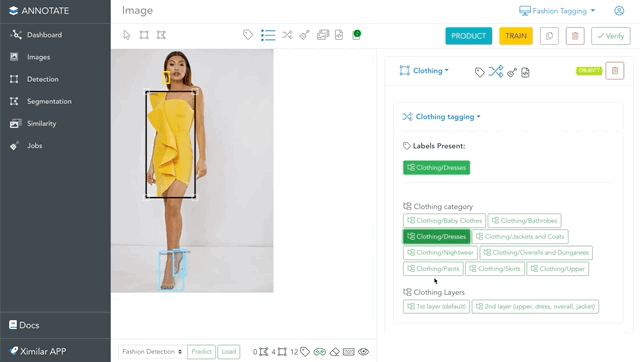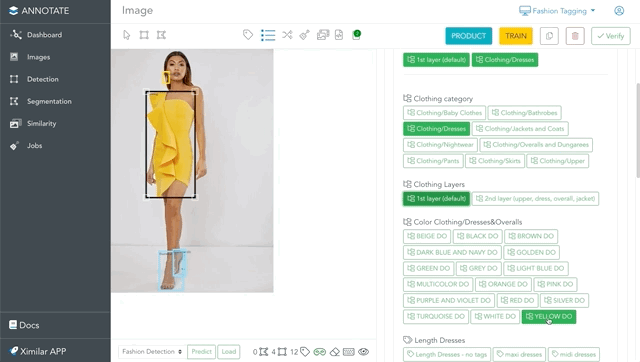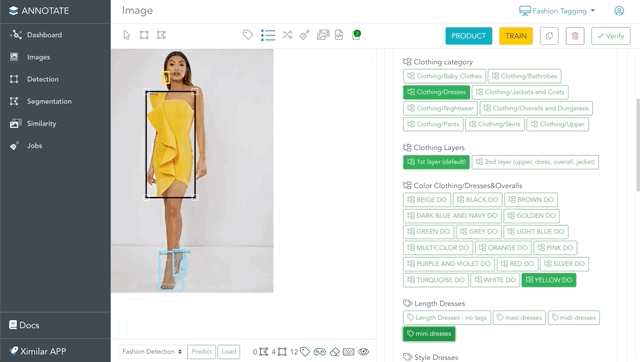
For example, in this image is a fashion object “Clothing”, to which we need to assign more labels. Adding the Clothing/Dresses label will expand the tags that are in the Length Dresses and Style Dresses tasks. If you select the label Elegant from Style Dresses, only features & attributes you need will be suggested for annotation.
Automate Repetitive Tasks With AI
Annotate was initially designed to speed up the work when building computer vision solutions. When annotating data, manual drawing & clicking is a time-consuming process. That is why we created the AI helper tools to automate the entire annotating process in just a few clicks. Here are a few things that you can do to speed up the entire annotation pipeline:
- Use the API to upload your previously annotated data to train or re-train your machine learning models and use them to annotate or label more data via API
- Create bounding boxes and polygons for object detection & instance object segmentation with one click
- Create jobs, share the data, and distribute the tasks to your team members
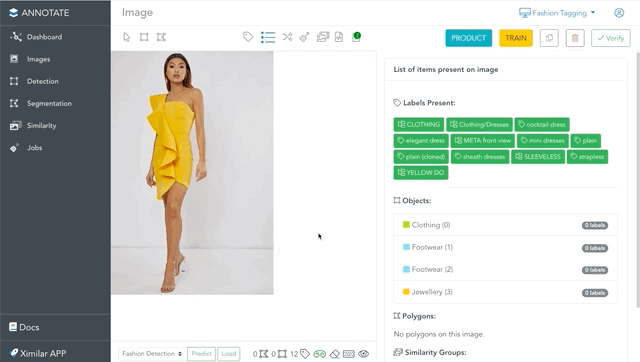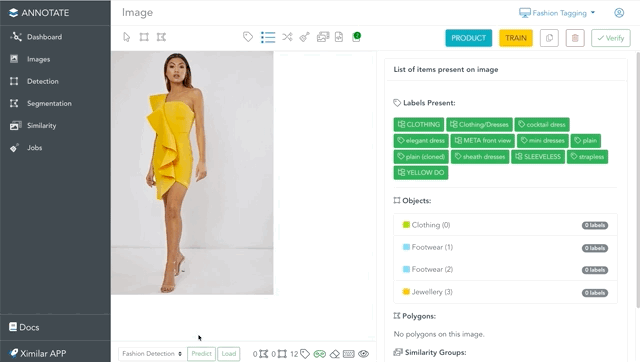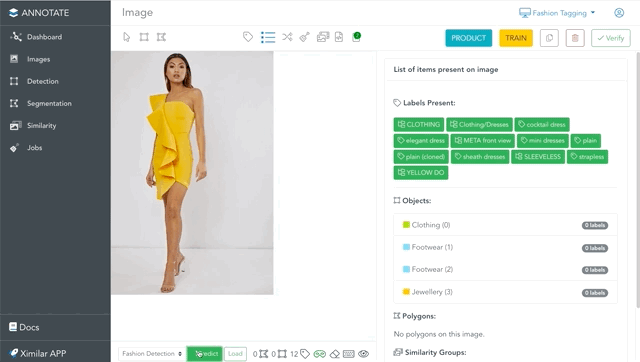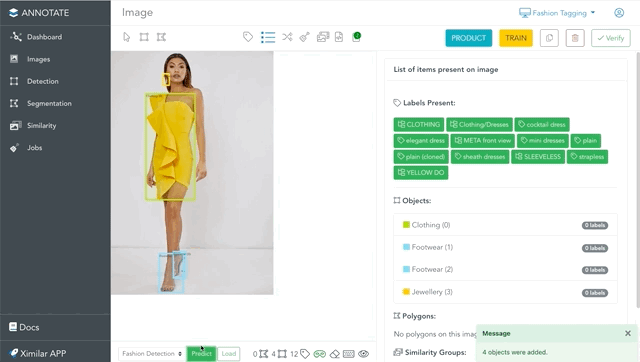
Image Annotation Tool for Advanced Visual AI Training
As the main focus of Ximilar is AI for sorting, comparing, and searching multimedia, we integrate the annotation of images into the building of AI search models. This is something that we miss in all other data annotation applications. For the building of such models, you need to group multiple items (images or objects, typically product pictures) into the Similarity Groups. Annotate helps us create datasets for building strong image similarity search models.
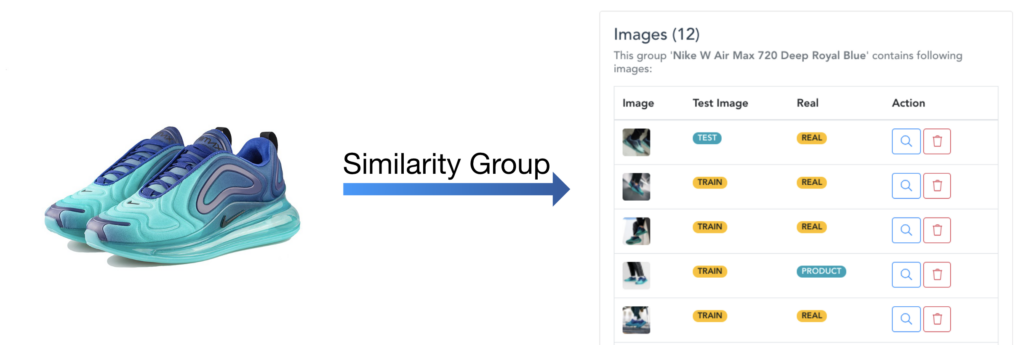
Annotate is Always Growing
Annotate was originally developed as our internal image annotation software, and we have already delivered a lot of successful solutions to our clients with it. It is a unique product that any team can benefit from and improve the computer vision models unbelievably fast.
We plan to introduce more data formats like videos, satellite imagery (sentinel maps), 3D models, and more in the future to level up the Visual AI in fields such as visual quality control or AI-assisted healthcare. We are also constantly working on adding new features and improving the overall experience of Ximilar services.
Annotate is available for all users with Business & Professional pricing plans. Would you like to discuss your custom solution or ask anything? Let’s talk! Or read how the cooperation with us works first.
Tags & Themes
Related Articles
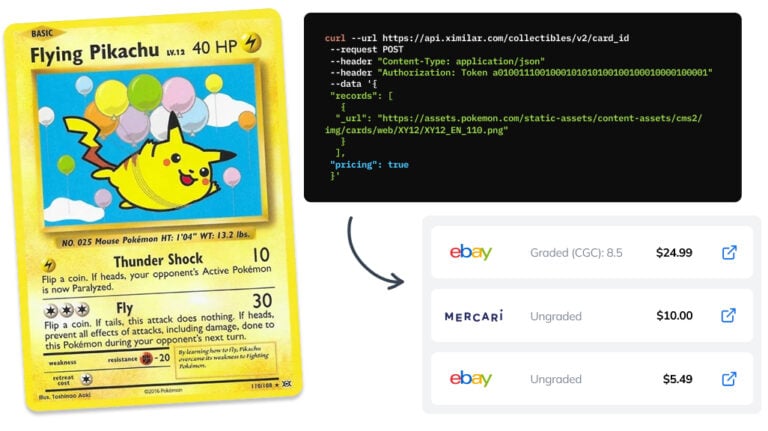
How to Automate Pricing of Cards & Comics via API
A step-by-step guide on how to easily get pricing data for databases of collectibles, such as comic books, manga, trading card games & sports cards.
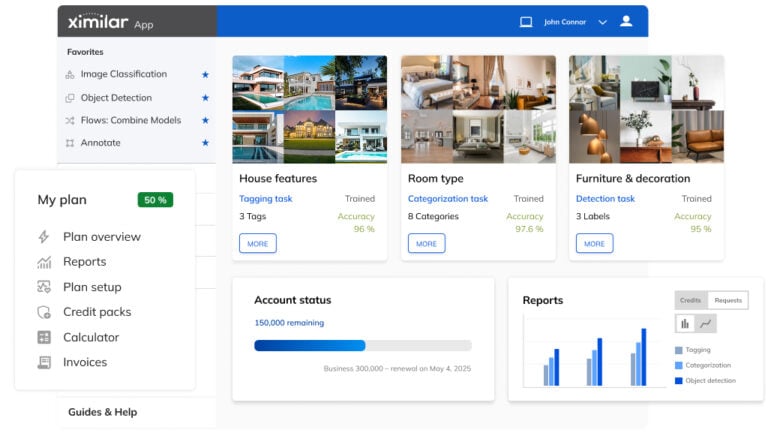
Getting Started with Ximilar App: Plan Setup & API Access
Ximilar App is a way to access computer vision solutions without coding and to gain your own authentication key to use them via API.

Get an AI-Powered Trading Card Price Checker via API
Our AI price guide can be used for value tracking of cards and comic books, offering accurate pricing data and their history.

